
When the firm produces zero output, the cost is $1000. When they increase output to 220, the cost rises to $4200. The marginal cost is falling and so the firm is facing diminishing returns to the variable factor.Ī firm produces 200 units and the total cost of production is $4000. The firm is producing in the short run and so is not facing returns to scale. The firm is facing diminishing returns as the marginal cost is falling. Please select an answer No, that's not right. Increasing returns to the variable factorĭiminishing returns to the variable factor When output rises to 240, the cost rises to $4100. Divide the total cost by the level of output and we get $19.10.Ī firm producing in the short run produces 200 units and the total cost of production is $4000. Have you divided by 200 units rather than 220 units? Yes, that's correct. This is the total cost, you need to divide by the level of output to get average cost. What is the average cost of producing 220 units? Have you divided the increase in cost by the increase in output correctly?Ī firm produces 200 units and the total cost of production is $4000. The marginal cost is the cost of one more unit (increase in cost of $200, from an increase in output of 20 equals $10 per unit). The marginal cost is the cost of one more unit. When output rises to 220, cost goes up by $200, but the marginal cost is the cost of one more unit.
Section 1.5 Theory of the firm - questions.1.5 Theory of the firm - notes (HL only).Section 1.4 Market failure - simulations and activities.1.3 Government intervention - simulations and activities.1.3 Government intervention - questions.Section 1.2 Elasticities - simulations and activities.1.1 Competitive markets - simulations and activities.1.1 Competitive Markets: Demand and Supply - notes.1.1 Competitive Markets: Demand and Supply.Topic pack - Microeconomics - introduction.Since all inputs can change in the long-run, there is no long-run average fixed cost curve. This is why we have a flat total fixed cost curve and constantly declining average fixed cost curve.
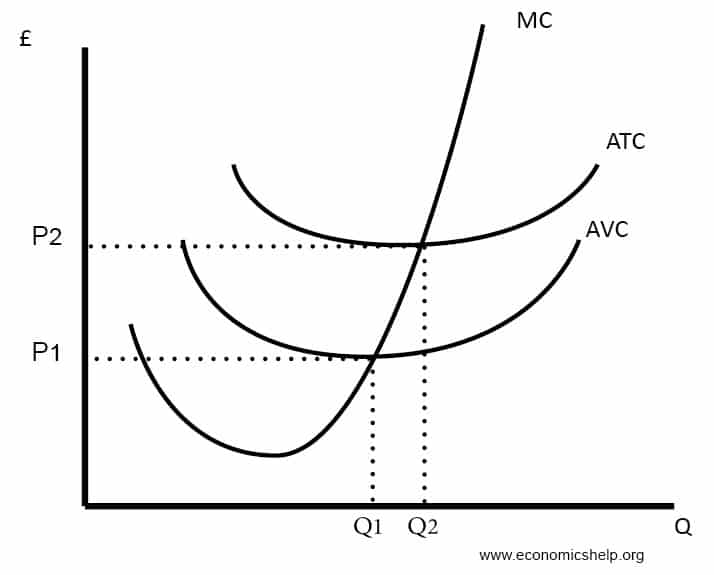
If we plot the total fixed cost and average fixed cost for Sucrose Farms, we will get the following graph:Īs output increases, total fixed cost remains the same but the average fixed cost falls indefinitely. Please note that the cost of pesticides is not a fixed cost because it varies with change in production level. Since its total production is 1,200 tons, average fixed cost of $129.2 per ton ($155,000/1,200). ($25,000 × 3) for labor, $60,000 on account of farming equipment rent and $20,000 on account of depreciation). Sucrose Farms total fixed cost in the short-run is $155,000 (i.e. The business' total output is 1200 tons of sugar cane. They have to apply insecticides and pesticides which costs $1,000 per square kilometer. The depreciation they charge on the farm building and the farm fencing is $20,000 per annum. They have also obtained some farming equipment for which they pay a $60,000 rent per annum. They pay a salary of $25,000 per annum to each worker. They have hired 3 workers on a one-year contract which is non-cancelable. Sucrose Farms is engaged in cultivation of sugar cane. FormulaĪverage fixed cost (AFC) equals total fixed cost (FC) divided by output (Q): Typical examples of fixed costs include salaries of permanent employees, rent paid on non-cancellable lease, mortgage payments on plant and machinery, etc. Since all inputs are variable in the long-run, no costs are fixed in the long-run. Short-run is defined as a time period in which at least one of the inputs, typically capital, is fixed. Average fixed cost is relevant only in the short-run. Whether a cost is fixed or variable depends on whether we are considering a cost in short-run or long-run. AFC is calculated by dividing total fixed cost by the output level. Fixed costs are such costs which do not vary with change in output. In economics, average fixed cost (AFC) is the fixed cost per unit of output.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
